Human Performance Lab
VO2 Testing | Cardiogenic Autonomic Neuropathy Testing | Exercise Stress Testing
VO2 Testing
VO2 testing is a process commonly used with elite athletes to determine their optimal training zones for fat metabolism and cardiovascular training. It is a common measurement used to establish the aerobic endurance of an athlete prior to or during the course of training. It is one of several tests used to determine an athlete’s cardiovascular fitness and performance capacity. It is measured in milliliters of oxygen used in one minute per kilogram of body weight (mL/kg/min). It is based on the premise that the more oxygen an athlete consumes during high-level exercise, the more the body will generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) energy in cells.
- The point (known as your aerobic base heart rate) at which your body still uses fat as its dominant fuel.
- The highest sustainable intensity of exercise, known as your anuerobic threshold, that your body can sustain and still burn fat efficiently.
- The rate at which your body absorbs oxygen, which your body requires to burn fat. Studies have shown that a VO2 less than 28 indicates increased health issues.
Metabolic Testing
Primarily used for weight-loss purposes, but there’s more to it than that. Metabolic testing is a process that allows you to discover what is the maximum amount of calories you can consume in a day and still lose weight. This easy test measures your Resting Metabolic Rate or RMR. Your RMR is the number of calories you would burn doing nothing but resting all day. The majority of all calories burned (about 70 to 80%) are burned at the resting level.
Through metabolic testing, you have taken the first step towards making your metabolism work for you. Understanding your body’s metabolism will give you the tools to lose fat while retaining muscle and to know exactly how many calories you need to eat to lose weight or maintain weight. In order to lose weight, you must burn more calories than you consume.
A metabolic assessment measures several things:
- The amount of calories your body needs to function, including everything from regulating your body’s hormones to thinking thoughts.
- The amount of calories you need to consume each day to achieve your fitness goal, whether that’s a weight loss goal or greater athletic performance.
Cardiogenic Autonomic Neuropathy Testing
Despite its high prevalence in individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM) neuropathies are the most underdiagnosed and undertreated diabetic chronic complication. The involvements of somatic and autonomic nerve fibers in DM present complex pathophysiologies. The impairment of sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) leads to autonomic neuropathy, a condition that may affect different organ systems such as cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and visual. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN), occurs when there is an impairment of autonomic control of the cardiovascular system after ruling out other causes of dysautonomia. Patients with complaints of dizziness or lightheadedness or those with Parkinsons Disease may benefit from Autonomic Neuropahty Testing which we perform in the office.
Read blog about New CV Testing at Sarasota Wellnes »
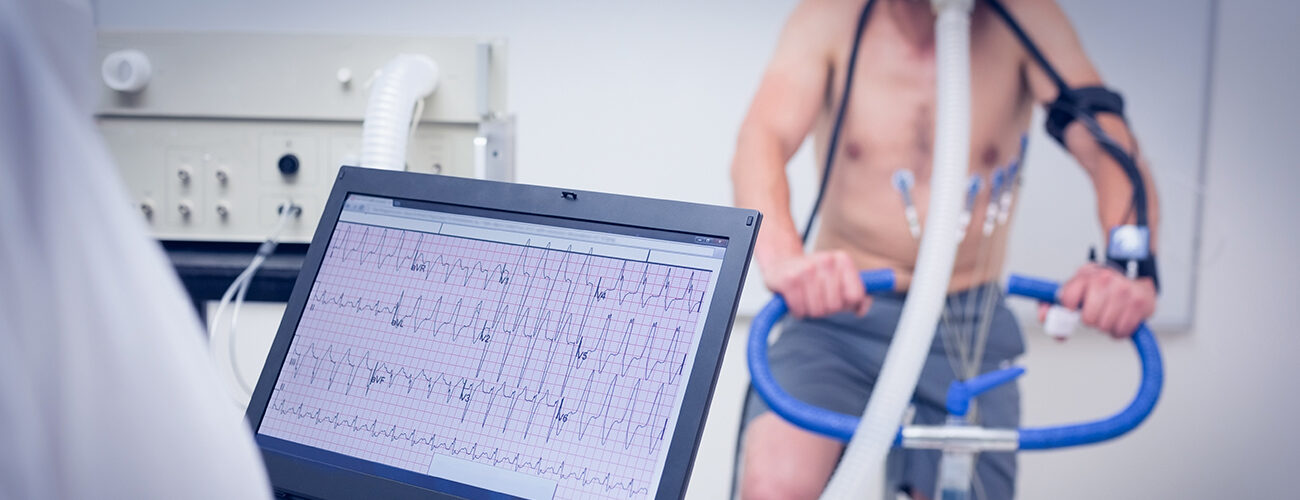
Exercise Stress Testing
- is hooked up to equipment to monitor the heart.
- walks slowly in place on a treadmill. Then the speed is increased for a faster pace and the treadmill is tilted to produce the effect of going up a small hill.
- may be asked to breathe into a tube for a couple of minutes.
- can stop the test at any time if needed.
- afterwards will sit or lie down to have their heart and blood pressure checked.
